
CYBER SYRUP
Delivering the sweetest insights on cybersecurity.
Stop Asking AI Questions, and Start Building Personal AI Software.
Feeling overwhelmed by AI options or stuck on basic prompts? The AI Fast Track is your 5-day roadmap to solving problems faster with next-level artificial intelligence.
This free email course cuts through the noise with practical knowledge and real-world examples delivered daily. You'll go from learning essential foundations to writing effective prompts, building powerful Artifacts, creating a personal AI assistant, and developing working software—all without coding.
Join thousands who've transformed their workflows and future-proofed their AI skills in just one week.
Iranian State-Sponsored Hackers Target Israeli Cyber Experts in Sophisticated Phishing Campaign
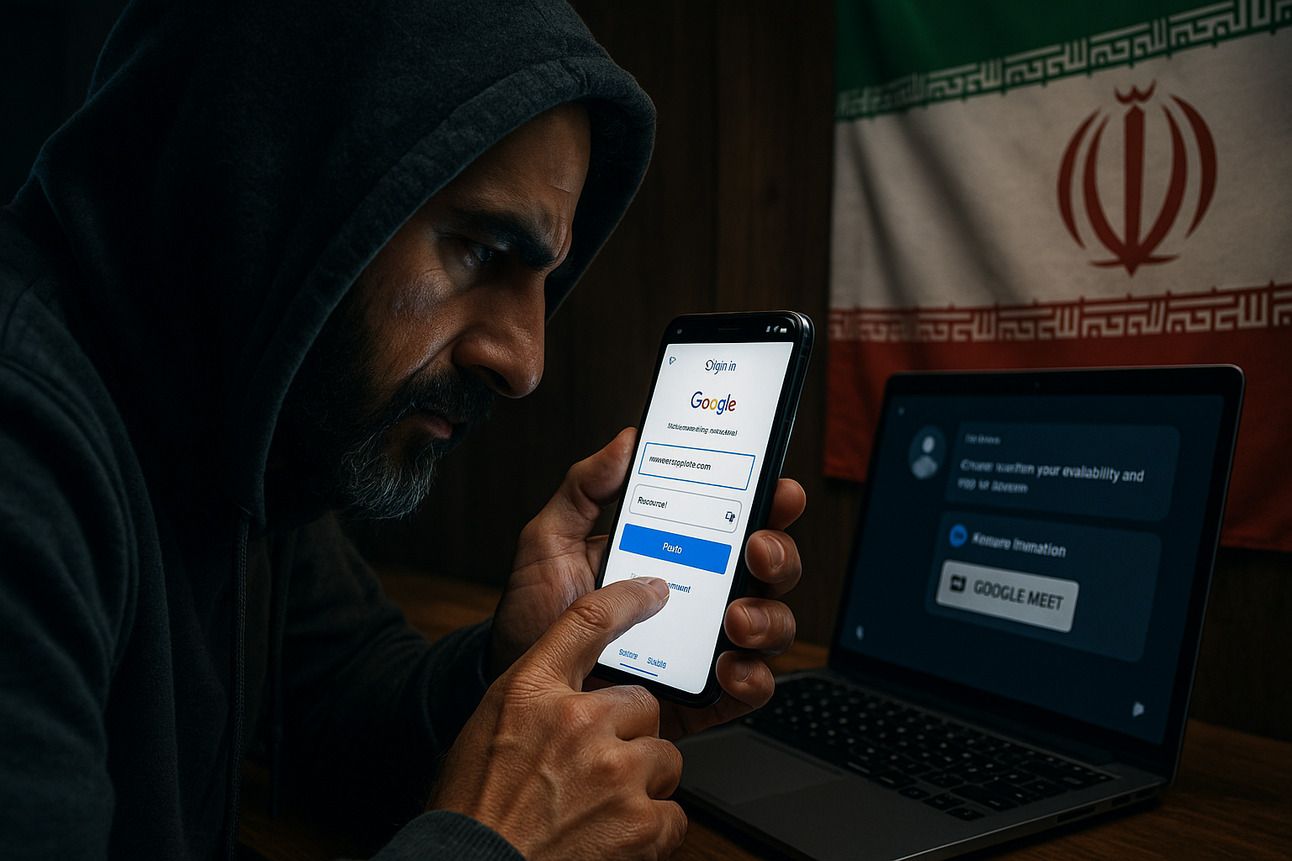
Cybersecurity researchers have uncovered a new spear-phishing campaign conducted by an Iranian state-sponsored threat group associated with the Islamic Revolutionary Guard Corps (IRGC). The campaign, observed in mid-June 2025, targets high-profile Israeli individuals in the cybersecurity, journalism, and academic sectors.
Campaign Overview
According to a recent report from Check Point Research, the group—tracked as Educated Manticore—employed social engineering tactics by impersonating assistants to tech executives or researchers. The attackers reached out to victims through email and WhatsApp messages, pretending to invite them to meetings or collaborate on cybersecurity initiatives. These messages, often AI-generated, leveraged current geopolitical tensions to make the outreach more convincing.
Once trust was established, the attackers directed the victims to phishing pages that mimicked Google login and Google Meet interfaces. These fake pages were meticulously designed to steal credentials and two-factor authentication (2FA) codes.
Threat Actor Attribution
Educated Manticore overlaps with several known Iranian advanced persistent threat (APT) groups, including:
APT35 (Charming Kitten)
APT42
Magic Hound
Mint Sandstorm (formerly Phosphorus)
TA453
Yellow Garuda
These groups are known for using fictitious online personas on platforms like LinkedIn, Facebook, and WhatsApp to deceive targets and deploy malware or steal sensitive information.
Technical Details
The phishing infrastructure employed modern web development frameworks, including React-based Single Page Applications (SPA), to replicate Google login flows convincingly. Features of the phishing kit included:
Pre-filled email addresses for authenticity
Real-time WebSocket communication to exfiltrate credentials
Passive keylogging to capture incomplete login attempts
2FA capture and relay capabilities
Some fake pages were hosted on Google Sites with decoy Google Meet visuals. Clicking on these elements redirected users to phishing pages designed to bypass scrutiny and trigger the credential theft process.
Implications and Response
The campaign reflects the evolving sophistication of Iranian cyber operations. Check Point notes that the rapid deployment of domains and infrastructure, coupled with swift takedowns when discovered, showcases the threat actors’ agility and determination.
“Educated Manticore continues to pose a persistent and high-impact threat, particularly to individuals in Israel during the escalation phase of the Iran-Israel conflict,” Check Point warned.
Staying Protected
To mitigate risk from such campaigns:
Be cautious of unsolicited communications, especially those invoking urgency or sensitive geopolitical topics.
Avoid clicking on links from unknown or unverified sources.
Enable multi-factor authentication (MFA) and monitor for phishing attempts designed to bypass it.
Use email filtering tools and inspect URLs before entering credentials.

